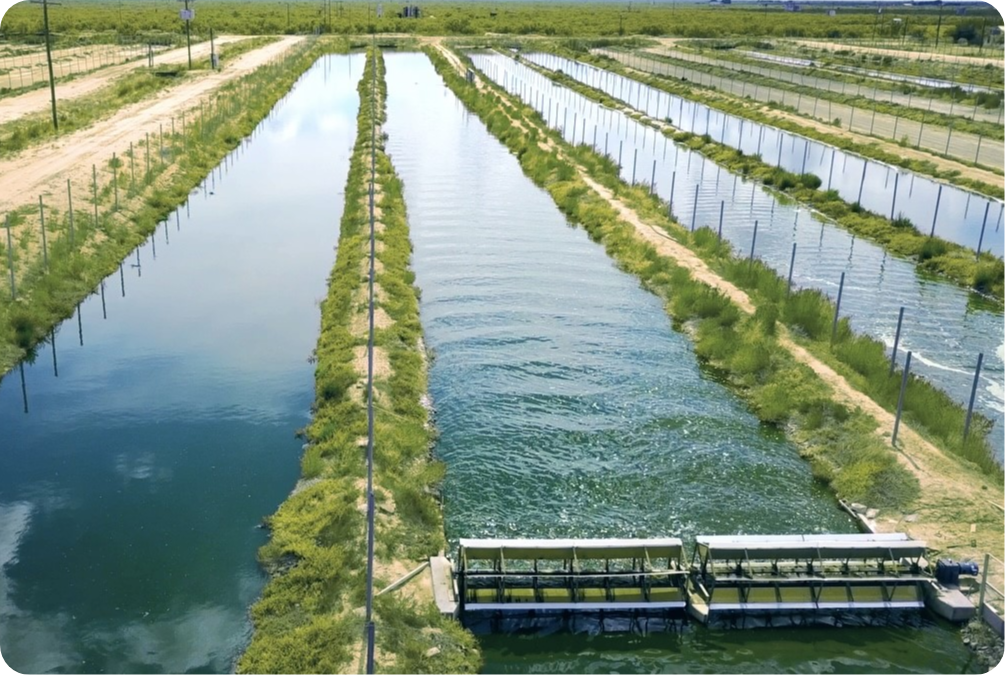
We grow our own algae in Texas
for our omega-3 supplements
The brilliance of 𝘪𝘸𝘪 𝘭𝘪𝘧𝘦
Grounded in Science: We developed technology to bind polar lipids with omega-3 fatty acids for superior absorption.*
Made with Integrity: Our sun-grown algae, cultivated in the US desert, transforms barren land and non-potable water into a powerhouse of nutrition.
Planet-Friendly Nourishment: Unlock a world of wellness and sustainability with our holistic approach, supporting both your health and the vitality of our planet’s fish populations for a brighter future.
 Science-based
Science-based
-

 New
NewOmega-3 Sport
A higher DHA blend to support post-exercise muscle recovery.Regular price From $22.99Regular priceSale price From $18.39 $22.99Unit price perSale -
Omega-3 Essential
Essential fatty acids to nourish you every day.Regular price From $17.99Regular priceSale price From $14.39 $17.99Unit price perSale
why iwi life is better
+Plant sources such as flax, hemp, chia, and ahiflower contain a short-chain precursor to true Omega-3 called ALA. They do not provide true DHA and EPA like algae does.
for you, and the planet

our algae is grown in controlled environments, without relying on wild fish populations. This reduces pressure on marine ecosystems and helps conserve fish stocks.

our algae farming requires fewer resources such as fresh water and land compared to traditional fishing operations. It also produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions and minimizes habitat destruction associated with fishing activities.
By using algae as a direct source of omega fatty acids, we reduce the need to harvest wild fish, which helps protect marine biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Algae omegas, cultivated in controlled environments, naturally have lower levels of heavy metals and pollutants than fish.

Our algae-based omega supplements offer a plant-based source of essential fatty acids for vegans and vegetarians, without relying on animal-derived products.
customer reviews
See All Reviewsavailable at